What is SCADA Software?
Published on Aug 18, 2024 | Category: BasicShare this Page:
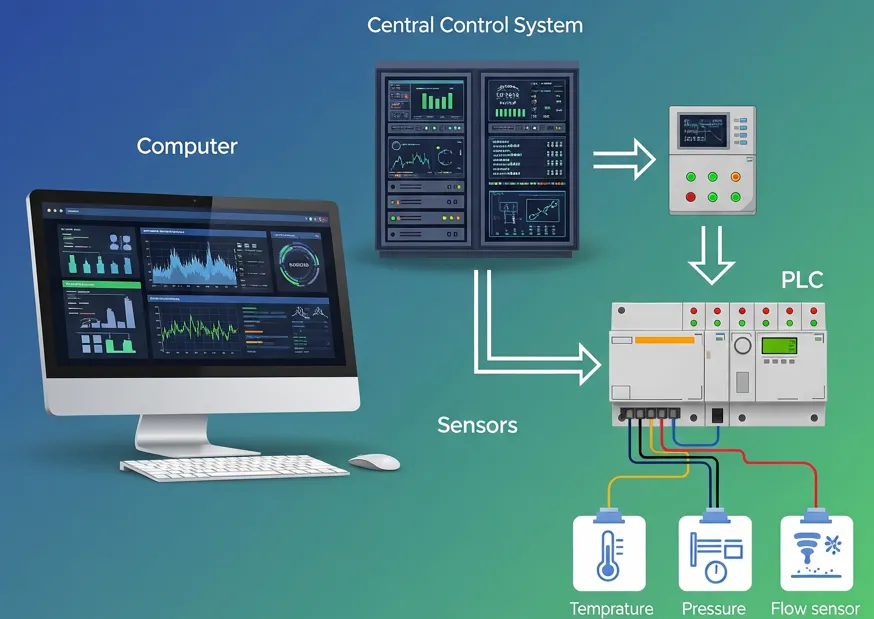
SCADA software, or Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, is an essential tool used in industrial automation for monitoring, controlling, and analyzing processes in real time. It acts as the bridge between operators and field devices, allowing industries to visualize data, receive alarms, and make quick decisions to keep plants running efficiently.
The role of SCADA software goes beyond simple monitoring. It provides centralized control of distributed assets, data logging for performance tracking, historical analysis for optimization, and advanced alarm management for safety. With its user-friendly graphical interface, operators can interact with PLCs, sensors, and other devices seamlessly.
This page explains what SCADA software is, its importance in industrial environments, and how to select the right SCADA system based on project size, hardware compatibility, communication protocols, and cost-effectiveness. Whether you are new to automation or an experienced professional, this guide will help you understand the fundamentals of SCADA and make better choices for your applications.
What is SCADA?
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. It is an industrial software system used to monitor, control, and analyze real-time processes in factories, plants, and large-scale infrastructure such as power grids, water treatment facilities, and oil & gas pipelines.
SCADA provides a centralized platform where operators can view live data from sensors and PLCs, receive alarms, control equipment remotely, and store historical data for performance analysis. In simple terms, SCADA connects machines, sensors, and controllers with humans, making complex processes easier to manage and safer to operate.
What is SCADA Software?
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) software is an industrial automation tool that helps monitor, control, and analyze real-time processes. It connects to devices like PLCs, RTUs, and sensors to collect live data from machines, equipment, and plants.
The main role of SCADA software is to give operators a clear visualization of processes on their screens, generate alarms when something goes wrong, and store historical data for reporting. This makes it easier to manage large and complex industrial systems safely and efficiently.
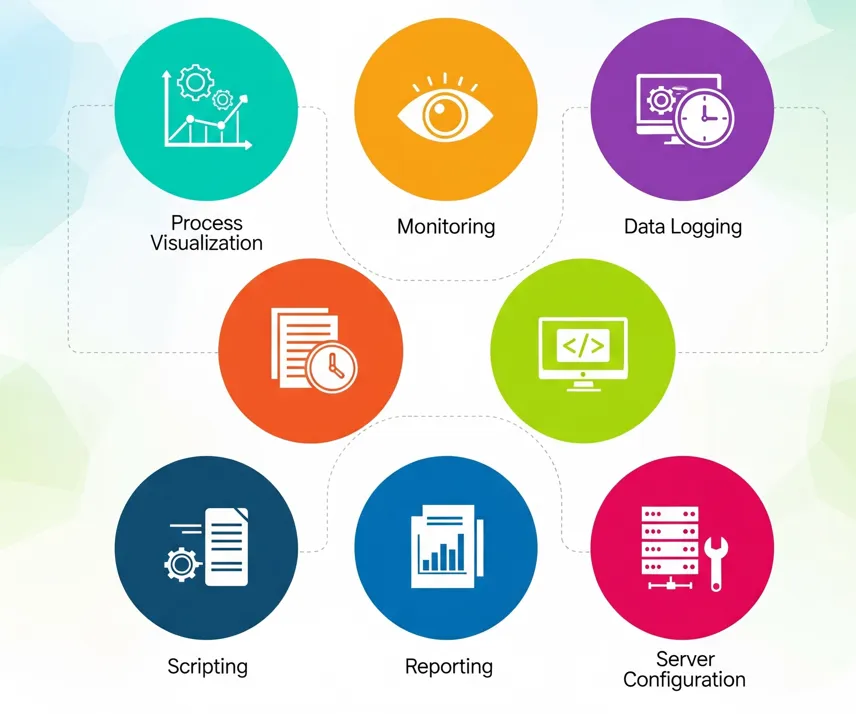
Functions of SCADA Software
SCADA software is designed to provide full visibility, control, and data management of industrial processes. It combines real-time monitoring, visualization, and analysis to ensure plants operate efficiently and safely. Below are the key functions:
- Process Visualization: Provides graphical displays of machines, pipelines, and plant processes in real-time for operators.
- Monitoring: Continuously checks field devices like PLCs, RTUs, and sensors to ensure smooth operations.
- Data Logging: Records process values, alarms, and system events for analysis and future reference.
- Scripting & Automation: Allows custom logic and automatic control actions through built-in scripting languages.
- Alarm Management: Generates alarms and notifications whenever parameters exceed safe limits.
- Reporting: Produces customized reports on production, efficiency, downtime, and maintenance.
- Server Configuration: Centralized setup to manage SCADA servers, communication drivers, redundancy, and networking.
- Historical Data Storage: Maintains a database of trends, performance records, and archived process information.
- Remote Access: Enables monitoring and control of plants from remote locations via web or mobile interfaces.
- Security Management: Provides user authentication, role-based access, and cyber-security protection.
Top SCADA Software with Manufacturers
Different industries use SCADA software depending on their requirements for process control, monitoring, and data management. Below is a list of the most popular SCADA software packages and their manufacturers:
- Siemens WinCC (TIA Portal / PCS7): A widely used SCADA system from Siemens, offering seamless integration with Siemens PLCs and advanced visualization tools.
- AVEVA Wonderware (InTouch): Developed by AVEVA (formerly Schneider Electric), known for its user-friendly interface and strong industrial connectivity.
- GE iFIX (HMI/SCADA): From GE Digital, offering powerful process visualization, data collection, and secure plant automation solutions.
- Ignition SCADA: Developed by Inductive Automation, a modern SCADA platform that supports unlimited tags, web-based access, and strong IIoT integration.
- ABB 800xA SCADA: From ABB, widely used in process industries like oil & gas, chemical, and power plants with strong redundancy and safety features.
- Rockwell Automation FactoryTalk View: A SCADA solution tightly integrated with Allen-Bradley PLCs, providing scalable visualization and reporting.
- Movicon SCADA: An advanced SCADA/HMI system by Emerson (Progea), popular for energy, water, and building automation industries.
- Honeywell Experion SCADA: From Honeywell, designed for critical process industries with high reliability and cybersecurity features.
- Schneider Electric EcoStruxure Geo SCADA Expert: A SCADA solution for infrastructure, energy, and utility sectors with advanced alarm handling.
- Yokogawa FAST/TOOLS: A flexible and web-based SCADA software used in power generation, water, and oil & gas applications.
These SCADA systems are selected based on their global usage, industrial support, and ability to integrate with different PLCs, RTUs, and field devices.
Applications of SCADA Software
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) software plays a vital role in modern industries by enabling real-time monitoring, control, and automation of processes. Its applications span across multiple domains where efficiency, reliability, and safety are critical. Below are the key applications of SCADA systems:
- Manufacturing Automation: Used in factories for production line control, machine monitoring, and quality assurance.
- Power Generation & Distribution: SCADA monitors substations, transformers, grid health, and ensures uninterrupted electricity supply.
- Oil & Gas Industry: Controls drilling operations, pipeline monitoring, tank level management, and leak detection.
- Water & Wastewater Management: Automates pump stations, water treatment plants, reservoir levels, and distribution systems.
- Building Automation: Used for HVAC control, lighting management, and smart building energy efficiency.
- Transportation Systems: Railway signaling, traffic light control, and airport operations monitoring.
- Food & Beverage Industry: Controls batch processing, packaging lines, and temperature monitoring for quality standards.
- Pharmaceuticals: SCADA ensures compliance by monitoring clean rooms, process parameters, and production validation.
- Renewable Energy: Supervises wind farms, solar power plants, and energy storage systems.
- Mining & Metals: Used for conveyor belt monitoring, crusher controls, and ore processing optimization.
In short, SCADA software applications are found in almost every industrial sector where continuous process monitoring and control are essential. With advanced data logging, alarms, and reporting features, SCADA ensures higher productivity, safety, and regulatory compliance.
How to Select SCADA Software
Choosing the right SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) software is an important decision for industries looking to improve automation, efficiency, and real-time monitoring. Since every industry has unique requirements, the selection of SCADA software should be based on technical features, scalability, budget, and long-term support. Below are the key factors to consider:
- Industry Requirements: Identify whether the SCADA system will be used for power, manufacturing, water treatment, oil & gas, or building automation. Each industry may need specialized features.
- Compatibility: Ensure the software is compatible with your existing PLCs, DCS, and field devices. Check for support of standard protocols like Modbus, OPC, and Ethernet/IP.
- User Interface: A simple, customizable, and intuitive HMI (Human Machine Interface) is essential for operators to quickly understand and respond to system data.
- Scalability: Choose software that can grow with your business — from a single-site installation to enterprise-wide monitoring.
- Real-Time Data Handling: Look for fast data acquisition, reliable logging, trending, and alarm management features.
- Cybersecurity: Modern SCADA must have strong security features like role-based access, encrypted communication, and compliance with IT standards.
- Vendor Support & Training: Select a trusted vendor with 24/7 technical support, documentation, and training availability.
- Cost & Licensing: Evaluate the licensing model (per tag, per server, or per client) and balance features with your budget.
- Integration with IT/OT Systems: Check if it integrates smoothly with ERP, MES, databases, and cloud platforms for Industry 4.0 readiness.
- Reporting & Analytics: Advanced SCADA software provides customizable reports, dashboards, and predictive maintenance insights.
In summary, selecting SCADA software involves balancing technical capability, ease of use, cybersecurity, and future scalability. A careful evaluation will ensure the system meets both current and future automation needs.