If-Else Conditions in Structured Text (ST) – RSLogix 5000 & Studio 5000 Programming
Published on Aug 19, 2025 | Category: if elseShare this Page:
In RSLogix 5000 / Studio 5000 Structured Text (ST) programming, an
If-Else condition is a fundamental decision-making statement used to
control program execution based on logic. It checks whether a condition is
TRUE or FALSE, and depending on the result, the PLC executes one
block of instructions or another.
We use If-Else statements in Structured Text because they make complex logic easier to manage compared to Ladder Logic. Instead of relying on long rungs with multiple contacts and coils, you can directly write clear
text-based conditions. This approach simplifies motor control, safety
checks, alarms, interlocks, and decision-based sequences in industrial
automation.
By using If-Else conditions in Structured Text, programmers can reduce ladder
clutter, increase readability, and implement advanced logic such as
nested conditions, loops, and calculations. This makes it one of
the most powerful tools for Allen-Bradley PLC programming inside
RSLogix 5000 / Studio 5000.
What is If-Else in Structured Text?
In Structured Text (ST) programming for RSLogix 5000 / Studio 5000, the If-Else statement is a conditional instruction that lets the PLC make decisions. It checks if a condition is TRUE; if so, the defined action executes. If the condition is FALSE, the program can either do nothing or follow an alternate action defined by the ELSE or ELSIF branch.
You use IF...THEN to complete an action when specific conditions occur, such as turning on a motor, starting a timer, or triggering an alarm. If the condition is not met, the ELSE part allows you to define what should happen instead.
This makes If-Else in Structured Text similar to decision-making statements in traditional programming languages, but adapted for industrial control systems. It improves readability and is especially useful for handling complex logic without long ladder diagrams.
Expression of If-Else in Structured Text
The If-Else expression in Structured Text is written using logical conditions that evaluate to TRUE or FALSE. Based on the result, the PLC executes the corresponding block of code.
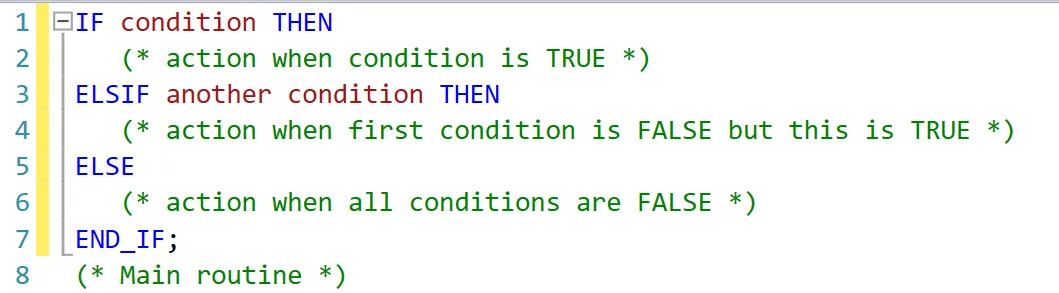
- condition: Any logical expression (e.g., Temp > 50, Motor_On = TRUE)
- THEN: Defines what action should happen when the condition is met
- ELSIF: (optional) Allows checking multiple conditions in sequence
- ELSE: (optional) Defines the default action when none of the conditions are TRUE
- END_IF: Closes the If-Else block
What is IF Statement in Structured Text (Without ELSE)?
The IF statement in Structured Text is used to perform an action only when a specific condition is TRUE. Unlike If-Else, it does not provide an alternative action if the condition is FALSE. This makes it very useful for simple checks where only one action is required.

In this example:
- Start_PB is a push button input (Boolean).
- Motor_Run is a motor output tag (Boolean).
- When the push button is pressed (Start_PB = TRUE), the motor starts (Motor_Run := TRUE).
- If the push button is not pressed, the PLC simply does nothing (no ELSE action).
The above image shows a simple IF statement in Studio 5000 Structured Text (ST) where only a single action is executed when a condition is TRUE. This is the most basic form of conditional logic in ST.
What is IF-ELSE Condition in Structured Text?
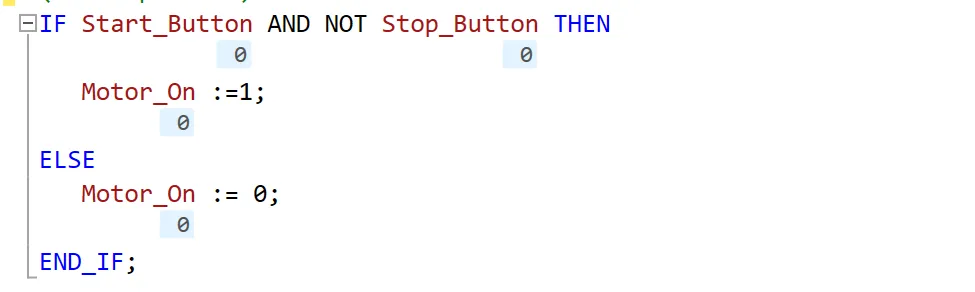
The IF-ELSE statement in Structured Text (ST) is used to perform one action when a condition is TRUE, and a different action when the condition is FALSE. It provides a complete decision-making structure, making it more flexible than a simple IF statement.
-
In this example:
- The motor will run only when Start_Button is pressed
- AND Stop_Button is not pressed.
- If Stop_Button is pressed, the motor immediately stops
- regardless of the Start button status.
- This type of control is commonly used in industrial motor circuits.
The above image shows an IF-ELSE condition in Studio 5000 Structured Text (ST). With IF-ELSE, you can design powerful decision-making logic for machine control, safety interlocks, and conditional operations.
What is Multiple IF-ELSE (ELSIF) Condition in Structured Text?
In Structured Text (ST), you can use ELSIF statements when you need to check more than one condition in sequence. This is similar to Else If in traditional programming languages.
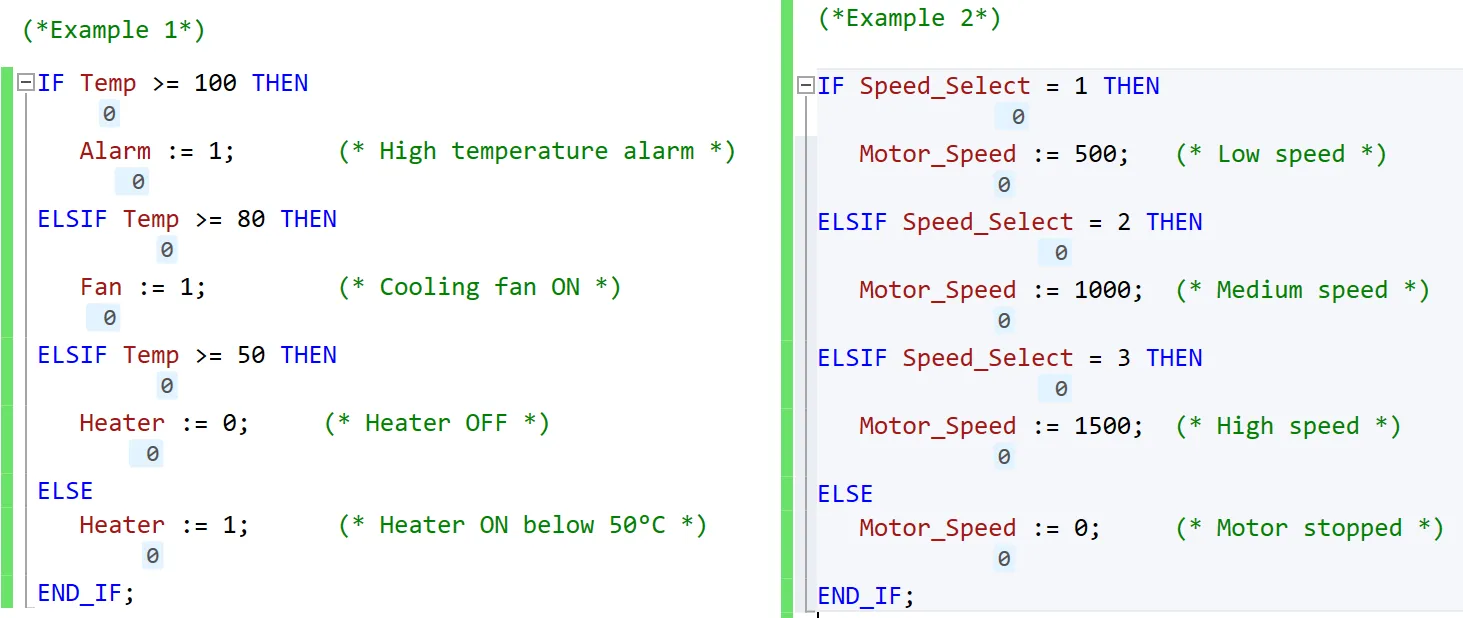
Example 1 – Temperature Control System
-
Explanation:
- If temperature is >= 100, the alarm is activated.
- If not, but temperature is >= 80, the fan runs.
- If not, but temperature is >= 50, the heater is turned off.
- Otherwise, if below 50, the heater is turned on.
Example 2 – Motor Speed Selection
Explanation:
- Based on the Speed_Select value, the motor runs at different speeds.
- If no valid selection is made, the motor stops.
The above image shows how multiple IF-ELSE conditions (with ELSIF) are used in Studio 5000 Structured Text (ST) to handle complex decision-making logic in industrial automation.
What is Nested IF-ELSE in Structured Text?
A Nested IF-ELSE condition means placing one IF statement inside another IF. This is useful when you need to check a second condition only if the first condition is already true.
General Syntax:
IF condition1 THEN
IF condition2 THEN
(* action when condition1 AND condition2 are TRUE *)
ELSE
(* action when condition1 is TRUE but condition2 is FALSE *)
END_IF;
ELSE
(* action when condition1 is FALSE *)
END_IF;
Example 1 – Motor Control with Safety
Explanation:
Example 2 – Tank Level Control
-
Explanation:
- First check if the Tank_Level is greater than or equal to 80%.
- If yes, then check if there is no pump fault (Pump_Fault = 0).
- If both are true, pump starts; otherwise, an alarm is triggered.

The above image demonstrates how nested IF-ELSE structures are used in Studio 5000 Structured Text programming to create safer and more reliable automation logic.
Conclusion – When to Use IF, IF-ELSE, ELSIF, and Nested IF-ELSE in Structured Text
In Studio 5000 Structured Text (ST), conditional statements allow you to make decisions and control program flow. Each type of condition has its best use case:
- IF (without ELSE): Used when you only need to check a single condition and perform an action if it is true. Example: Turn ON a motor only when Start_Button is pressed.
- IF-ELSE: Used when you need to perform one action if the condition is true, and a different action if it is false. Example: Run motor if Start_Button is pressed, otherwise stop it.
- ELSIF: Best when you have multiple conditions to check in sequence, instead of writing several nested IF statements. Example: Control fan speed based on temperature ranges.
- Nested IF-ELSE: Used when a second condition should only be checked if the first condition is true. This is common in safety checks or multi-step logic. Example: Start pump only if Tank_Level is high AND no fault is active.
- Use IF for simple checks.
- Use IF-ELSE when two opposite outcomes are required.
- Use ELSIF when checking multiple conditions in order.
- Use Nested IF-ELSE when conditions depend on each other.
Choosing the right structure keeps your Structured Text program clean, readable, and reliable for industrial automation tasks in RSLogix 5000 or Studio 5000.