Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB): Working Principle, Types, and Applications
Published on July 09, 2025 | Category: IntroductionShare this Page:
A Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB) is an essential electrical device used to protect motors from common faults like overcurrent, short circuits, phase failure, and undervoltage (with UVR). It combines multiple functions such as overload protection, short circuit interruption, ON/OFF switching, and manual reset—all in a single compact unit. MPCBs are widely used in industrial and commercial setups where electric motors play a critical role in powering machines and processes. Brands like Havells offer reliable MPCB solutions designed specifically for motor safety and efficiency.
Electric motors are vital components in today’s automated industries, and ensuring their long service life requires effective electrical protection. MPCBs provide this by acting quickly against abnormal conditions, preventing potential damage and downtime. These breakers come in various types and ratings to suit different motor sizes and applications. In this article, we will explain how MPCBs work, their internal protection mechanisms, how to size them correctly, and how to select the right model based on your motor's load and usage.
It's important to understand the difference between an MPCB and a motor starter. While MPCBs are focused on providing protection against electrical faults, motor starters are primarily responsible for starting and stopping the motor—either manually or automatically—while offering basic protection. In many systems, both components are used together: the MPCB handles protection, while the starter manages control. With the right combination of MPCB and motor starter, you can ensure both safe operation and efficient motor management in any industrial electrical setup.
What is MPCB?
A Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB) is an electromechanical device designed to protect electric motors from damage due to overload, short circuits, phase failures, and undervoltage conditions. It combines motor protection, manual switching, and automatic disconnection in one unit. MPCBs are specifically built to match the requirements of motor protection, making them more effective than standard MCBs or fuses in motor circuits.
Working Principle of MPCB
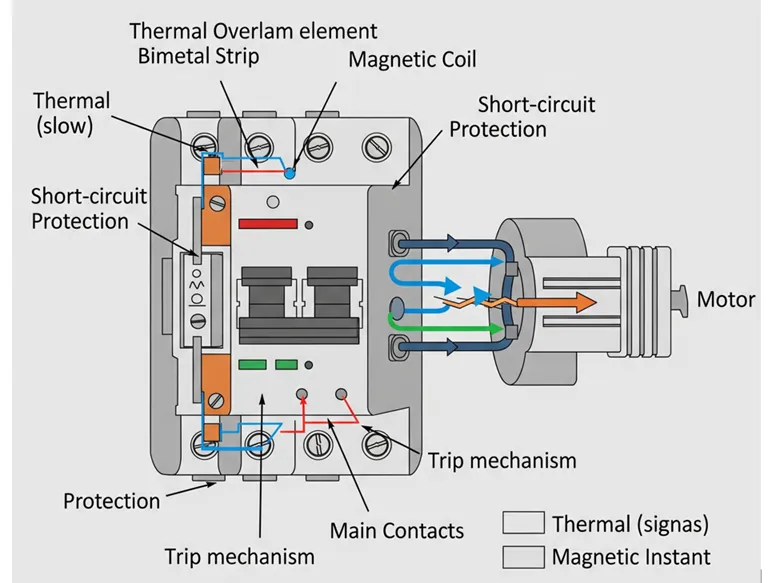
The MPCB works using a combination of thermal and magnetic protection mechanisms. The thermal element detects prolonged overcurrent (overload) and trips the breaker by bending a bimetallic strip. The magnetic element reacts instantly to high fault currents like short circuits using an electromagnet to trip the circuit immediately. Some MPCBs also include phase failure and undervoltage protection, ensuring complete motor safety.
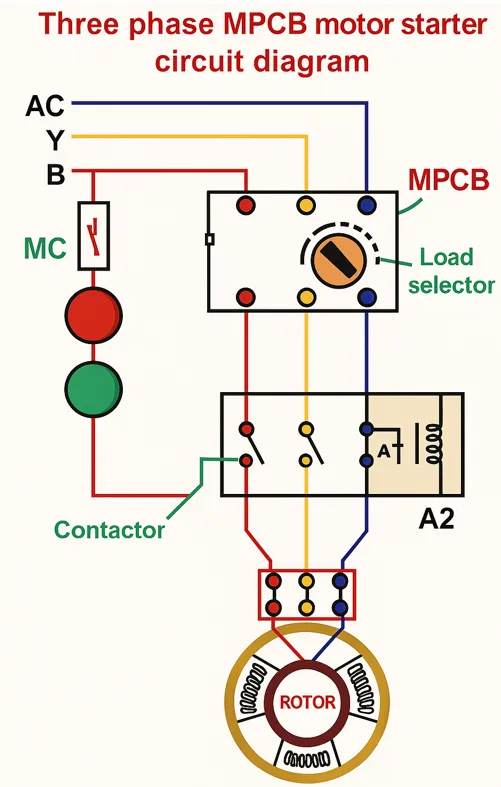
What Are the Functions of MPCB?
Motor Protection Circuit Breakers (MPCBs) serve multiple critical functions in motor control and protection systems. They not only safeguard motors from electrical faults but also assist in operational reliability and safety. The key functions of an MPCB include:
- Protection Against Electrical Faults: Provides protection from short circuits, line-to-ground faults, and other dangerous conditions.
- Overload Protection: Trips the circuit if the motor draws current beyond its rated limit for a prolonged period.
- Phase Unbalance and Phase Loss Protection: Detects and disconnects the motor when there is an imbalance or complete loss of one or more phases.
- Thermal Delay Function: Introduces a time delay before the motor can restart after an overload, allowing the motor to cool down.
- Motor Circuit Switching: Enables manual ON/OFF control of the motor circuit.
- Fault Signaling: Provides indication or signaling when a fault has occurred, improving diagnostics and maintenance response.
- Automatic Reconnection (in advanced models): Allows the system to automatically reconnect the motor after temporary disturbances are cleared.
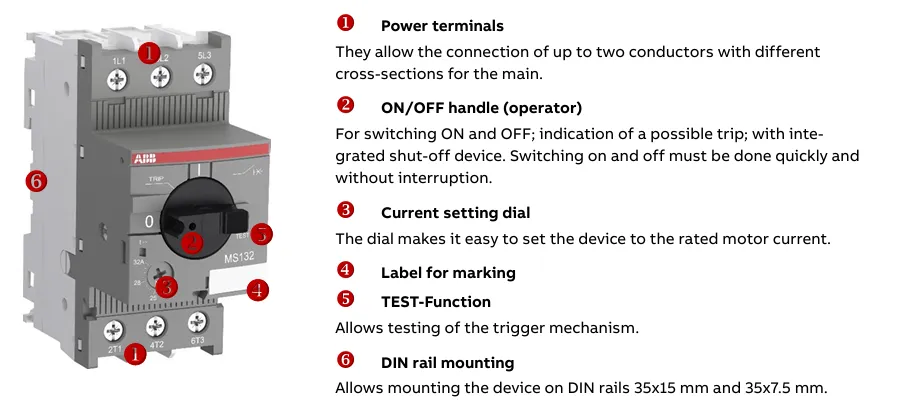
what is Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB) parts and its function
A Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB) is made up of several key components that work together to detect faults and protect electric motors. Below are the main parts of an MPCB with a brief explanation of each:
- a) Thermal Overcurrent Release: A bimetallic strip that bends when heated due to prolonged overcurrent, causing the breaker to trip and protect the motor from overload.
- b) Electromagnetic Overcurrent Release: An electromagnet that responds instantly to high short-circuit current and activates the trip mechanism to disconnect the circuit.
- c) Main Contact System: These are the primary contacts that carry the motor current and open to interrupt power during faults.
- d) Auxiliary Switch Position: These are additional contacts used for signaling, control, or status monitoring (e.g., trip status or breaker ON/OFF).
- e) Switch Latch: A mechanical latch that holds the breaker in the ON position and releases during a fault to allow tripping.
- f) Arcing Chamber: A specially designed area with arc splitters that safely extinguish the arc formed when the contacts open during fault conditions.
- g) Plunger Armature: Part of the electromagnetic mechanism; it moves when a short-circuit current is detected to activate the tripping system.
- h) Differential Trip Slide: A mechanical slide that enables tripping in case of phase imbalance or single phasing by detecting differences in magnetic force between phases.
Connection Diagram of 3 Phase Motor with MPCB and Indicator Lamps
This wiring diagram shows how to connect a 3-phase motor using an MCCB, MPCB, and two indicator lamps (red and green) for status indication. Each component has a specific role to ensure safe operation and easy troubleshooting.
1. Power Supply through MCCB
- The MCCB (Moulded Case Circuit Breaker) receives 3-phase supply: R (Red), Y (Yellow), B (Blue), and Neutral (Black).
- These wires are connected to L1, L2, L3, and N terminals of the MCCB.
- The output terminals of the MCCB are connected to the input of the MPCB.
2. MPCB Wiring and Function
- The MPCB (Motor Protection Circuit Breaker) protects the motor from overcurrent and short circuits. It also has ON/OFF switching capability.
- It has 3 input terminals (L1, L2, L3) connected from the MCCB output and 3 output terminals going to the motor (U, V, W).
- The MPCB includes auxiliary contacts: NO (Normally Open) and NC (Normally Closed).
3. Indicator Lamps Connection
- Red Lamp (START): Connected to the NO contact. It glows only when the MPCB is turned ON and the motor is running.
- Green Lamp (STOP): Connected to the NC contact. It glows only when the MPCB is OFF and the motor is stopped.
- Both lamps are connected to the neutral wire for completing the circuit.
4. Motor Connection
- The output of the MPCB is connected directly to the motor terminals: U, V, and W.
- Each phase R, Y, B is delivered to one of the motor windings for 3-phase operation.
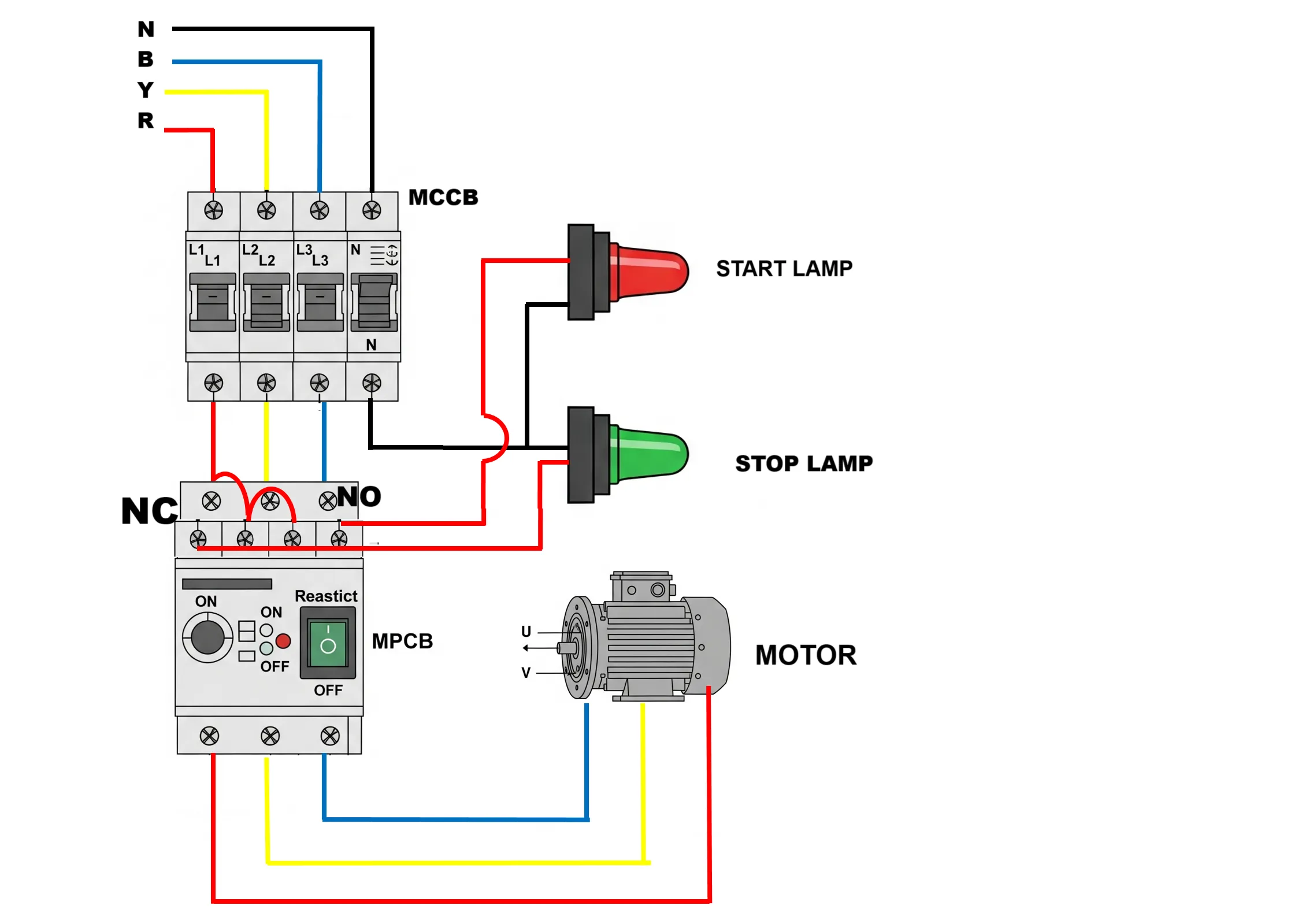
Working Principle
When the MCCB is switched ON, 3-phase supply is sent to the MPCB. If the MPCB is in OFF condition, the NC (Normally Closed) contact allows current to flow to the green lamp, indicating the motor is OFF. When the MPCB is switched ON:
- The NO (Normally Open) contact closes, lighting the red lamp to show the motor is running.
- The NC contact opens, switching off the green lamp.
- At the same time, the 3-phase power flows through the MPCB to the motor terminals (U, V, W), starting the motor.
Conclusion
This circuit is widely used for motor control in industries. It provides:
- Overload and short circuit protection (via MPCB)
- Manual ON/OFF control
- Status indication using lamps
- Isolation and safety via MCCB
How Does an MPCB Work?
A Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB) operates by using both thermal and magnetic mechanisms to protect electric motors from different types of electrical faults. Here's how it works:
- Thermal Protection: MPCBs use a bimetallic strip that bends due to heat when an overload condition occurs. This bending action trips the breaker to prevent motor overheating.
- Magnetic Protection: In the case of a short circuit, line-to-ground fault, or other high-current fault, an internal electromagnet instantly triggers the trip mechanism. This provides rapid disconnection to prevent serious damage.
- Phase Monitoring: Advanced MPCBs can detect abnormalities between phase voltages. If a phase failure or imbalance is detected, the MPCB disconnects the motor immediately to avoid motor burnout or mechanical stress.
Why MPCB Used in Electrical Systems?
An MPCB (Motor Protection Circuit Breaker) is used to protect electric motors from common electrical faults that can damage the motor or affect operational efficiency. It provides integrated protection against:
- Overload: Prevents motor overheating from continuous overcurrent.
- Short Circuit: Instantly trips the circuit to stop high fault currents.
- Phase Failure: Disconnects the motor in case one or more phases are missing.
- Undervoltage: With an undervoltage release (UVR), it disconnects the motor when voltage drops dangerously low.
How Does MPCB Provide Fuseless Motor Protection?
One of the key advantages of MPCBs is fuseless protection. Unlike traditional fuses that need replacement after a fault, MPCBs automatically disconnect the motor during a short circuit without the need to replace any component. This not only saves costs but also provides ultra-fast tripping—disconnecting the motor in less than 5 milliseconds when operating in the current-limiting range. This helps to minimize damage and improves the reliability of the system.
Why is MPCB Easy to Use for Maintenance Teams?
MPCBs are designed with ease of operation in mind. For plant maintenance teams, using MPCBs in motor feeders simplifies troubleshooting and improves response time. Their compact design, manual reset, and visual status indication make them ideal for industrial panels. They enhance availability, safety, and reliability in motor-driven systems—making them a preferred choice in modern motor protection schemes.
What Are the Types of Motor Protection Circuit Breakers (MPCBs)?
Motor Protection Circuit Breakers (MPCBs) come in different types depending on their protection mechanisms, settings, and application requirements. Below are the main types of MPCBs used in electrical motor control systems:
- Thermal Magnetic MPCB: This is the most commonly used type. It combines a thermal element for overload protection and a magnetic element for short-circuit protection. It is suitable for all types of motors and provides reliable protection in most industrial and commercial applications.
- Electronic MPCB: These use electronic sensing and control circuits to provide accurate and adjustable protection. Electronic MPCBs offer better precision, customization, and sensitivity compared to traditional models, making them ideal for modern motor protection systems.
- Adjustable MPCB: This type allows the user to manually adjust the current trip settings based on the motor’s operating conditions. It provides flexibility and is useful when motor loads vary or need fine-tuned protection.
- Fixed MPCB: Fixed MPCBs come with pre-set protection limits defined by the manufacturer. They are cost-effective and easy to use but offer less flexibility in setting adjustments.
What Are the Applications of Motor Protection Circuit Breakers (MPCBs)?
MPCBs are widely used in various industrial and commercial sectors to ensure the safe and reliable operation of electric motors. They play a critical role in preventing motor failure due to overload, short circuits, and phase loss. Below are some common applications of MPCBs:
- Industrial Motor Control Panels: MPCBs are used to protect motors running conveyor belts, pumps, compressors, mixers, and fans in manufacturing plants.
- Water Pumping Stations: They ensure reliable operation and protection of motors used in water supply systems and irrigation units.
- HVAC Systems: Used to protect motors in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems from electrical faults and overheating.
- Building Automation: MPCBs are integrated into motor circuits in elevators, escalators, and other automated systems in commercial and residential buildings.
- Agricultural Equipment: They protect motors used in automated irrigation systems, grain dryers, and other electrically powered farming equipment.
- Renewable Energy Systems: MPCBs are also used in solar and wind installations to protect motors involved in tracking, pumping, or cooling operations.
How to Select the Correct Size for an MPCB?
Selecting the appropriate size for a Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB) is critical for ensuring that your motor is well-protected while avoiding unnecessary tripping during normal operations. A properly sized MPCB offers a balance between safety, responsiveness, and system reliability.
Instead of simply matching the motor's current rating, it's recommended to choose an MPCB rated slightly above the motor's full-load current. This prevents false tripping during startup or under minor load fluctuations, especially in motors with high inrush currents.
Thermal settings on the MPCB should be tuned to reflect the motor's expected operating conditions. These settings help protect against slow-rising overloads, and the tripping curve should align with the motor's thermal tolerance. For fault protection, the magnetic trip level must be set high enough to allow safe motor startup but low enough to respond instantly in case of a short circuit.
When sizing an MPCB, consider environmental conditions, motor starting type (DOL, star-delta, soft starter), duty cycle, and safety standards. Oversizing can leave motors unprotected, while undersizing can result in frequent downtime. Always refer to manufacturer charts or datasheets for optimal trip range selection.